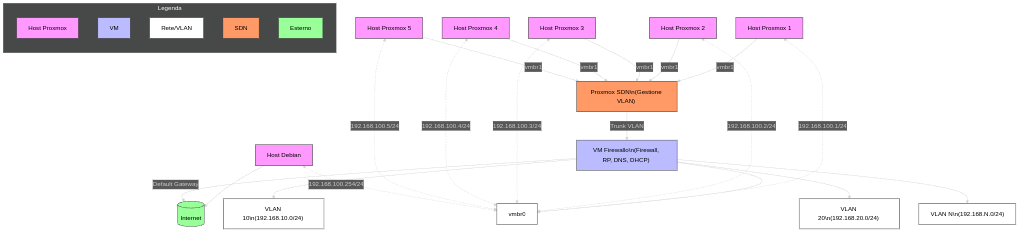
Architettura
graph TD
%% Stile
classDef host fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,color:#000;
classDef vm fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,color:#000;
classDef network fill:#fff,stroke:#333,color:#000;
classDef sdn fill:#f96,stroke:#333,color:#000;
classDef external fill:#9f9,stroke:#333,color:#000;
%% Nodi fisici
Host1[Host Proxmox 1]:::host
Host2[Host Proxmox 2]:::host
Host3[Host Proxmox 3]:::host
Host4[Host Proxmox 4]:::host
Host5[Host Proxmox 5]:::host
HostDebian[Host Debian]:::host
%% VM Firewallo
Firewallo["VM Firewallo\n(Firewall, RP, DNS, DHCP)"]:::vm
%% Reti e VLAN
VLAN_Management["vmbr0"]:::network
VLAN_1["VLAN 10\n(192.168.10.0/24)"]:::network
VLAN_2["VLAN 20\n(192.168.20.0/24)"]:::network
VLAN_N["VLAN N\n(192.168.N.0/24)"]:::network
Internet[(Internet)]:::external
%% SDN
SDN["Proxmox SDN\n(Gestione VLAN)"]:::sdn
%% Connessioni fisiche
Host1 ---|vmbr1| SDN
Host2 ---|vmbr1| SDN
Host3 ---|vmbr1| SDN
Host4 ---|vmbr1| SDN
Host5 ---|vmbr1| SDN
HostDebian --- Internet
%% Connessioni logiche
SDN ---|Trunk VLAN| Firewallo
Firewallo --- VLAN_Management
Firewallo --- VLAN_1
Firewallo --- VLAN_2
Firewallo --- VLAN_N
Firewallo ---|Default Gateway| Internet
%% Host fisici in VLAN Management
Host1 <-.->|192.168.100.1/24| VLAN_Management
Host2 <-.->|192.168.100.2/24| VLAN_Management
Host3 <-.->|192.168.100.3/24| VLAN_Management
Host4 <-.->|192.168.100.4/24| VLAN_Management
Host5 <-.->|192.168.100.5/24| VLAN_Management
HostDebian <-.->|192.168.100.254/24| VLAN_Management
%% Descrizione
subgraph Legenda
H1[Host Proxmox]:::host
V1[VM]:::vm
N1[Rete/VLAN]:::network
S1[SDN]:::sdn
E1[Esterno]:::external
end
-
Host Proxmox (5 nodi):
- Tutti connessi alla bridge
vmbr1che porta al Proxmox SDN (gestione centralizzata delle VLAN). - Appartengono alla vmbr0 per la gestione dei nodi fisici.
- Tutti connessi alla bridge
-
Host Debian:
- Funge da gateway verso Internet per i nodi fisici (non per le VM).
- Connesso alla stessa rete del vmbr0.
-
VM Firewallo:
- Firewall, Reverse Proxy, DNS, DHCP per tutte le VM.
- Gateway predefinito per tutte le VM (indipendentemente dalla VLAN).
- Connesso a tutte le VLAN tramite trunk (gestito da Proxmox SDN).
-
VLAN:
- VLAN Management: Solo per i nodi fisici (Proxmox + Debian).
-
Altre VLAN (es.
10,20,N): Per segmentare le VM (es. servizi web, database, ecc.). - Tutte le VLAN sono routed attraverso Firewallo.
-
Flusso Internet:
- Le VM escono verso Internet tramite Firewallo (che applica NAT/regole).
- I nodi fisici escono direttamente tramite l’Host Debian (bypassando Firewallo per la gestione).
-
Proxmox SDN:
- Gestisce il trunking delle VLAN verso Firewallo e gli host fisici.

No Comments